A complete guide to NGSS with everything you need to know about the Next Generation Science Standards.

The Next Generation Science Standards (NGSS) have transformed STEM education across the U.S. In this article, we’ll answer the most common questions about NGSS and explore what the Next Generation Science Standards are, their purpose and benefits, and how to find STEM curriculum for elementary and middle school that aligns with NGSS practices.
Whether you are a teacher, administrator, parent, or community member, this comprehensive guide will help you understand the impact of NGSS and how to introduce these standards to your school or district.
What is NGSS?
So what are the Next Generation Science Standards?
In simple terms, NGSS is an educational framework designed to give students a deeper understanding of science topics. It does this through hands-on learning, integrating science concepts and STEM subjects, and linking concepts sequentially across grade levels.
In addition to the framework of instruction, hundreds of NGSS standards reside on the Next Generation Science Standards website and can be searched by keywords, grade level, and science subject.
However, NGSS uses a unique set of vocabulary to organize and define its curriculum, so you might find it helpful to review the NGSS terminology later in this article.
How does NGSS differ from old science standards?
Traditional science education typically follows a grade-specific topical curriculum taught through direct instruction. This might have students studying earth science in 5th grade, physical science in 6th grade, and life science in 7th grade. While students are exposed to a wide variety of science concepts, they don’t spend a lot of time exploring the interconnectedness of these subjects and how technology, engineering, or mathematics might play a role in the science concepts they’re studying.
Rather than gaining a shallow understanding of many different science topics throughout their education, NGSS introduces students to science concepts gradually and encourages students to apply their knowledge through active learning activities like labs, challenges, and projects. NGSS-aligned curriculum also introduces the other subjects of STEM through various hands-on learning activities and exercises so that students can see how these science concepts are applied outside of the classroom.
With these education practices, combined with a cumulative approach to learning (building on concepts learned in previous grade levels), students gain a much deeper understanding of each science concept and learn valuable skills like critical thinking, creative problem-solving, and communication skills that can be applied to any discipline.
Knowledge vs. Performance
Another difference between traditional science education standards and the Next Generation Science Standards is the definition of what qualifies as a met standard. Traditionally, we measured how much students knew and what knowledge they retained.
With NGSS, the focus is shifted to student performance: Which skills have the students mastered? How well can they apply their knowledge?
This is best seen in the structure of the standards themselves, which are called Performance Expectations. (More on that below.)
Where did The Next Generation Science Standards come from? (The History of NGSS)
At the time of developing the Next Generation Science Standards in the early 2000s, academic performance in the sciences was slipping, and educators realized that students were not developing the STEM skills needed for the 21st century. Their focus in developing the NGSS was to transform K-12 science education and replace outdated standards with research-based educational standards designed for the modern world.
The Next Generation Science Standards were developed through a coordinated effort from education and research organizations and 26 state partners from departments of education and science. In 2013, the standards were officially finalized and have since been adopted by 20 states, with 24 other states using science education standards based on the NGSS framework.
Understanding NGSS Terminology

NGSS Domains: These are the general areas of science that are taught through the Next Generation Science Standards. With NGSS’s integrated approach, these domains are often integrated throughout the curriculum, and students build upon their knowledge year by year.
The four domains of NGSS include:
- Physical Sciences - The study of how matter and energy interact. This domain covers science concepts such as physics, chemistry, motion, and energy.
- Life Sciences - The study of living organisms and their biological processes. This domain includes science concepts like ecosystems, evolution, and the cells, structures, and functions of organisms.
- Earth and Space Sciences - The study of processes, systems, and interactions of Earth and the universe. This includes concepts such as geology, oceanography, astronomy, and space exploration.
- Engineering, Technology, and Applications of Science - This domain involves the application of scientific knowledge to design solutions using engineering and technology. Within this domain are skills such as defining problems, designing and testing solutions, and critical thinking.
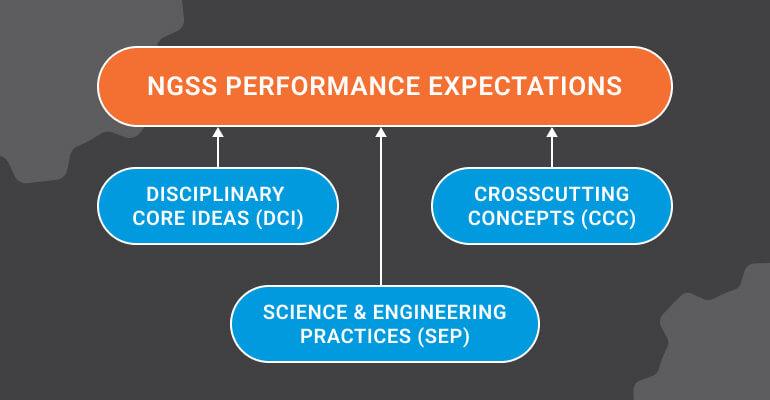
NGSS Performance Expectations (PEs): What students are expected to know and be able to do by the end of each level of instruction.
The Next Generation Science Standards are organized into a catalog of Performance Expectations (PEs). Each performance expectation is comprised of three dimensions to help students build proficiency in disciplinary knowledge, scientific skills, and the ability to connect that knowledge to other concepts.
The three dimensions of NGSS Performance Expectations include:
- Disciplinary Core Ideas (DCIs): The main science concept that students should understand. This is the “book knowledge” students learn to explain real-world phenomena.
- Science & Engineering Practices: These are skills that scientists and engineers use to investigate problems and solve them creatively. These practices include skills like asking questions, analyzing data, and designing models.
- Crosscutting Concepts (CCCs): These are the fundamental scientific concepts that connect all domains of science, such as cause and effect, patterns, logic, and systems.
Because every Performance Expectation includes each of these three dimensions, students benefit from a comprehensive learning experience that provides new knowledge, lets them practice new skills, and helps them connect their learning to other disciplines and activities outside the classroom.
At Kid Spark Education, each lesson plan provides the NGSS Performance Expectation that corresponds to the lesson material. You can browse our STEM lesson plans and curriculum tools here to see how NGSS is applied in our STEM lessons.
For example, our elementary lesson on Rotary Motion lists the learning objectives of the lesson plan and clearly defines the associated NGSS alignment:
What are NGSS storylines?
The Next Generation Science Standards utilize a tool called “Storylines” to help link key concepts across multiple grade levels. These storylines make it easier for students to revisit concepts from previous school years and add a more nuanced understanding as they develop those concepts further.
NGSS storylines also help educators. You can think of storylines like the “theme” of a series of lessons and activities.
At the elementary level, you might introduce a “Weather and Climate Storyline” that includes multiple lessons and activities across numerous grade levels.
Or middle schoolers might follow a “Forces and Motion Storyline” that introduces several different aspects of the physical sciences like motion, velocity, mass, and gravity.
The goal of NGSS storylines is to create a general topic of instruction that’s easy to refer back to. This helps students recall previous lessons and activities so they can build upon the knowledge and skills they’ve already learned in previous grade levels.

The 8 Science and Engineering Practices of NGSS
The Next Generation Science Standards are organized into eight different practices that can be applied to science education. These are designed to help students develop core science skills that can be used to investigate, understand, and change the world around them.
The eight NGSS practices include:
- Asking questions and defining problems: Students learn to ask questions and develop hypotheses about the world around them and how to identify problems that can be solved with engineering.
- Developing and using models: Students learn to build, draw, or use computational models to describe and predict events.
- Planning and carrying out investigations: To test their hypotheses, students learn how to conduct controlled scientific investigations using the scientific method through hands-on learning experiences.
- Analyzing and interpreting data: Students learn how to use the data they collect in their investigations by finding patterns, relationships, and possible sources of error.
- Using mathematics and computational thinking: Students learn how to apply mathematical concepts and tools to answer scientific questions. They also learn the foundations of logic and how to apply this to computer simulations and coding.
- Constructing explanations and designing solutions: Students learn how to construct logical explanations from their investigations and propose creative engineering solutions to solve problems.
- Engaging in argument from evidence: In addition to crafting explanations, students learn how to support their scientific conclusions and designs with both evidence and logical reasoning.
- Obtaining, evaluating, and communicating information: Students are taught the importance of presenting scientific information clearly and learning how to read, analyze, and interpret information clearly.
These practices are woven throughout the cumulative curriculum of the Next Generation Science Standards so that students develop a comprehensive understanding of the concepts they’re being taught, along with tools and skills that they can apply to their entire academic career.
In fact, a review of multiple research studies revealed that when STEM instruction incorporated NGSS practices, an increase in critical thinking, collaboration, motivation, and comprehension was seen across all four STEM subjects.
NGSS teaching practices inspire students to learn through interaction, and states that have adopted the Next Generation Science Standards into their curriculum have seen significant gains in student test scores and overall achievement.
NGSS Lesson Plan Examples for Elementary and Middle School
The NGSS Performance Expectations provide the framework for what students should know and which skills they should develop by grade level, but how to teach these standards is not included. That leaves ample room for creative lesson plans or NGSS-aligned curriculum programs like Kid Spark’s to bring these educational standards to your class.
To see what NGSS can look like in the classroom, we’ve provided some sample lesson plans for elementary and middle school.

Elementary NGSS Lesson Plan Samples
Designing Bird Feeders
NGSS Performance Expectation K-2-ETS1-2: Develop a simple sketch, drawing, or physical model to illustrate how the shape of an object helps it function as needed to solve a given problem.
Disciplinary Core Idea: Designs can be conveyed through sketches, drawings, or physical models
Science & Engineering Practice: Developing and using models
Crosscutting Concept: Structure and function
Sample Lesson: Using the framework of the Performance Expectation K-2-ETS1-2, you can create a lesson plan guiding students through designing and modeling a bird feeder. Provide your students with a list of criteria and constraints and a specific problem that needs to be solved, then have students create a drawing of their bird feeder design. They can then create a model of their design.
Investigating Sound Vibrations
NGSS Performance Expectation 1-PS4-1: Plan and conduct investigations to provide evidence that vibrating materials can make sound and that sound can make materials vibrate.
Disciplinary Core Idea: Sound can make matter vibrate, and vibrating matter can make sound.
Science & Engineering Practice: Planning and carrying out investigations
Crosscutting Concept: Cause and effect
Sample Lesson: Gather various noise-making materials such as tuning forks, drums, or hollow tubes, then gather various materials as samples of matter to be affected by sound vibrations like sand, water, or balloons. Create vibrating sounds with the various items around the different matter samples and have students record their observations and findings.
Middle School NGSS Lesson Plan Samples
Simple Machines: Inclined Plane
NGSS Performance Expectation MS-PS2-2: Plan an investigation to provide evidence that the change in an object’s motion depends on the sum of the forces on the object and the mass of the object.
Disciplinary Core Idea: The motion of an object is determined by the sum of the forces acting on it.
Science & Engineering Practice: Planning and carrying out investigations
Crosscutting Concept: Stability and change
Sample Lesson: In this Kid Spark lesson, students assemble an inclined plane and investigate how it’s used to multiply force. In your Kid Spark lab kit, you’ll be provided with step-by-step instructions, a curriculum packet, student workbooks, and reusable engineering components that can be used for this lesson and many others. Contact us today for more information about our NGSS-aligned STEM lab kits.
Nature’s Resources
NGSS Performance Expectation MS-LS2-1: Analyze and interpret data to provide evidence for the effects of resource availability on organisms and populations of organisms in an ecosystem.
Disciplinary Core Idea: Organisms depend on their environment for survival. Resource availability affects organism populations.
Science/Engineering Practice: Analyzing and interpreting data
Crosscutting Concept: Cause and effect
Sample Lesson: Gather various data sets of wildlife populations (some ideas might include tracking the population of endangered species, tracking the population of an animal when it’s been reintroduced to an area, etc). Discuss the patterns and trends in these populations with your students and have them create graphic representations of the relationships between each wildlife population and their food supply.
How to bring the Next Generation Science Standards into your classroom
The Next Generation Science Standards are designed to help students navigate the world of science by engaging with it. This helps students develop a deeper understanding of science concepts and sets them up for success throughout their academic careers.
Kid Spark Education has created a comprehensive STEM curriculum that aligns with NGSS standards and provides all the curriculum tools and training you need to confidently teach each lesson.
To explore more and speak with Kid Spark about bringing our lab kits to your classroom, contact us today.





